
Funk Kazimej
Kazimierz Funk (23 fevral 1884, Varşava, Polşa çarlığı – 20 noyabr 1967, Albani) — polşalı biokimyaçı idi və "vitamin" terminini ilk işlədən şəxs kimi tanınır. O, B1 vitamininin (tiamin) kəşfində mühüm rol oynayıb və digər vitaminlərin kəşfinə töhfə verib. Funkın işi qidalanma elminin inkişafında mühüm rol oynadı və beri-beri və pellaqra kimi xəstəliklərin qarşısının alınmasına və müalicəsinə kömək etdi.
== Həyatı ==
Kazimierz Funk 23 fevral 1884-cü ildə Polşanın Varşava şəhərində anadan olub. Atası həkim, anası isə evdar qadın idi. Funk Varşavada orta məktəbdə təhsil alıb və 1904-cü ildə tibb fakültəsinə daxil olub. O, 1907-ci ildə tibb fakültəsini bitirib və Bern Universitetində doktoranturaya başlayıb. O, “Vitaminlər kimyası” adlı mövzuda doktorluq dissertasiyası yazıb və 1911-ci ildə doktorluq dissertasiyasını alıb.
Funk postdoktorluq işini Londondakı Lister İnstitunda etdi. Burada beri-beri xəstəliyinin səbəbini araşdırmağa başladı.

Cüt və tək funksiyalar
"Funksiya" — Riyaziyyatın əsas anlayışlarından biri. Onun verilməsində sabit və ya dəyişən kəmiyyətlərdən istifadə edilir.
Müxtəlif ədədi qiymət ala bilən kəmiyyətə dəyişən kəmiyyət, yalnız bir ədədi qiymət ala bilən kəmiyyətə isə sabit kəmiyyət deyilir. Məsələn, havanın temperaturu, avtomobilin sürəti, dəniz suyunun səviyyəsi və s. dəyişən kəmiyyətlərdir. İlin fəsillərinin sayı, çevrənin uzunluğunun diametrinə olan nisbəti və s. sabit kəmiyyətdir. Çox zaman hər hansı kəmiyyətin bir qiyməti digər kəmiyyətin də, müəyyən qayda ilə ona uyğun hər hansı qiymət almasına səbəb olur. Onda ikinci dəyişən kəmiyyət birincidən asılı olur. Birinci dəyişənə sərbəst (asılı olmayan), ikinci dəyişənə isə asılı dəyişən deyilir.
Diferensiallanan funksiya
Əgər birdəyişənli, yaxud çoxdəyişənli
f
{\displaystyle f}
funksiyasının
P
{\displaystyle P}
nöqtəsində
d
f
{\displaystyle df}
diferensialı varsa, ona bu nöqtədə diferensiallanan funksiya deyilir.
D
{\displaystyle D}
oblastının hər bir nöqtəsində diferensiallanan
f
{\displaystyle f}
funksiyasına bu oblastda diferensiallanan funksiyası deyilir. Çoxdəyişənli
y
=
f
(
x
1
,
x
2
,
…
,
x
n
)
{\displaystyle y=f(x_{1},x_{2},\ldots ,x_{n})}
funksiyasının
P
{\displaystyle P}
nöqtəsində (
D
{\displaystyle D}
oblastında) diferensiallanan olması üçün bu nöqtədə (oblastda)onun bütün xüsusi törəmələrinin kəsilməz olması kifayətdir.
1. M. Mərdanov, S. Mirzəyev, Ş. Sadıqov Məktəblinin riyaziyyatdan izahlı lüğəti. Bakı 2016, "Radius nəşriyyatı", 296 səh.

Dirixle funksiyası
Dirixle funksiyası –
[
0
;
1
]
{\displaystyle [0;1]}
parçasında təyin olunmuş, arqumetin rasional qiymətlərində
0
{\displaystyle 0}
, arqumentin irrasional qiymətlərində
1
{\displaystyle 1}
qiymətini alan funksiya. Dirixle funksiyası
[
0
;
1
]
{\displaystyle [0;1]}
parçasının bütün nöqtələrində kəsilən funksiyadır. Bu funksiyanı alman riyaziyyatçısı Dirixlenin adı ilə bağlıdır. Dirixle funksiyası aşağıdakı kimi də təyin etmək olar:
lim
m
→
∞
(
lim
n
→
∞
cos
2
n
(
m
!
π
x
)
)
.
{\displaystyle \lim \limits _{m\rightarrow \infty }\left(\lim \limits _{n\rightarrow \infty }\cos ^{2n}(m!\pi x)\right).}
M. Mərdanov, S. Mirzəyev, Ş. Sadıqov Məktəblinin riyaziyyatdan izahlı lüğəti. Bakı 2016, "Radius nəşriyyatı", 296 səh.

Dirixlet eta funksiyası
Dirixlet eta funksiyası — Riyaziyyatda
η
(
s
)
=
(
1
−
2
1
−
s
)
ζ
(
s
)
{\displaystyle \eta (s)=\left(1-2^{1-s}\right)\zeta (s)}
olaraq təyin edilən funksiya. Burada ζ Rieman zeta funksiyasını göstərməkdədir.
Dövri funksiya
Təbiətdə və texnikada bəzi proseslər periodik olaraq təkrar olunur. Periodik dəyişən kəmiyyətləri öyrənmək üçün dövri funksiya anlayışından istifadə olunur.
Hər bir "x" ədədi ilə birlikdə "x-T" və "x+T" (T sıfırdan fərqli) ədədləri də "f" funksiyasının təyin oblastına daxildirlərsə və
f
(
x
−
T
)
=
f
(
x
)
=
f
(
x
+
T
)
{\displaystyle f(x-T)=f(x)=f(x+T)}
bərabərliyi ödənirsə, f funksiyasına dövrü T olan "dövri funksiya" deyilir.
0 (sıfır) istənilən funksiyanın dövrüdür. Dövrü "0" olan funksiyalar maraqlı deyil. Ona görə də T-ni sıfırdan fərqli qəbul edilir.
Dövri funksiyanın tərifi aşağıdakı teoremlərlə alınır.
"T" ədədi "f" funksiyasının dövrüdürsə "(-T)" ədədi də "f" funksiyasının dövri olur.
"T1" və "T2" ədədləri f funksiyasının dövrüdürsə
T1+T2 və
T1-T2 ədədləri də f funksiyasının dövrü olur.
T ədədi f funksiyasının dövrüdürsə, n istənilən tam ədəd olduqda "nT" ədədi də f funksiyasının dövrüdür.
Fizioloji funksiyalar
Fizioloji funksiyalar - insan, heyvan və bitki orqanizmlərinin, onların həyat fəaliyyətinin və ətraf mühitə uyğunlaşmalarının təmin edən müxtəlif istiqamətdəki fəaliyyəti.
Ətraf mühitdə rütubətin bolluğu şəraitində temperaturun aşağı olmasilə əlaqədar bitki köklərinin suyu sorma qabiliyyətinin azalması
Orqanizmlərin fasiləsiz fəaliyyətini saxlayan endogen bioloji ritmlər (ürək döyüntüsü, daxili sekresiyanın vəzifələrinin işi və s.)
Bitkinin və heyvanın belə həyaat dövründə maddələr mübadiləsi olduqca zəif gedir.
Orqanizmin fiziologiyasında dəyişkənlik.

Funksional
Əgər müəyyən
S
{\displaystyle S}
funksiyalar çoxluğundan götürülmüş hər bir
φ
{\displaystyle \varphi }
funksiyasına müəyyən bir
F
(
φ
)
{\displaystyle F(\varphi )}
ədədi qarşı qoyulursa, onda
S
{\displaystyle S}
çoxluğunda
F
{\displaystyle F}
funksionalı təyin edilmişdir. Başqa sözlə funksional qiymətləri ədədlərdən ibarət olan və funksiyalar çoxluğunda təyin olunmuş funksiyadır.
Məsələn,
[
0
;
1
]
{\displaystyle [0;1]}
parçasında təyin olunmuş kəsilməz funksiyalar sinfində
F
(
φ
)
=
φ
2
(
0
)
{\displaystyle F(\varphi )=\varphi ^{2}(0)}
qaydası ilə təyin edilmiş funksiya funksionaldır.
Xətti funksional adlanan, yəni
F
(
a
1
φ
1
+
a
2
φ
2
)
=
a
1
F
(
φ
1
)
+
a
2
F
(
φ
2
)
{\displaystyle F(a_{1}\varphi _{1}+a_{2}\varphi _{2})=a_{1}F(\varphi _{1})+a_{2}F(\varphi _{2})}
şərtini ödəyən funksional riyaziyyatda xüsusi əhəmiyyətə malikdir (burada
a
1
,
a
2
{\displaystyle a_{1},a_{2}}
ədədlər,
φ
1
,
φ
2
∈
S
{\displaystyle \varphi _{1},\varphi _{2}\in S}
). Xətti funksionalın təyin oblastı hökmən xətti fəza olmalıdır.
Funksional klavişlər
Funksional klavişlər (ing. function keys) — F1, F2, F3 və s. kimi nişanlanmış və klaviaturanın sol və ya yuxarı qırağı boyunca yerləşdirilmiş on və ya daha artıq sayda klaviş dəsti; bu klavişlər ayrı-ayrı proqramlarda xüsusi əməliyyatların yerinə yetirilməsi üçün istifadə olunur.
Funksional klaviş, mahiyyətcə, "qiyməti proqram" və ya bəzi hallarda istifadəçi tərəfindən müəyyənləşdirilən “proqramlaşdırılan” klavişdir. Yəni, proqramçı tərəfindən klavişə (düyməyə) xüsusi proqram tətbiq edilir. Funksional klaviş tətbiqi proqram və ya əməliyyat sistemi tərəfindən tez-tez rast gəlinən komandalar ardıcıllığını tez çağırmaq, ya da başqa bir yolla erişilməyən funksiyaya müraciət etmək üçün istifadə olunur. Belə ki, funksional klaviş (tək və ya digər klavişlərlə, məsələn, Control və ya Alt ilə kombinasiyada) verilmiş proqramın ekran arayışını çağıra bilər, kursorun yerini dəyişə bilər, xüsusi rejimi aktivləşdirə bilər və s.
F1 – Kömək pəncərəsinin açılması
F2 – Qovluğun və ya faylın adının dəyişdirilməsi
F3 – Cari qovluğda və ya Windows ƏS-də axtarış panelin açılması
F4 – Aktiv pəncərənin bağlanması
F5 – Qovluğun və ya faylın məzmunun yenilənməsi
F6 – Kursorun brauzerin adres sətirinə yerləşdirilməsi
F7 – Mətnin yoxlanışı
F8 – Windows ƏS yoxlanılan zaman yükləmə rejiminə icazə
F9 – Word sənədinin yenilənməsi
F10 – Pəncərənin menyusunun çağırışı
F11 – Tam ekranlı rejimə keçid
F12 isə Word proqramında yaddaşa vermək komandası üçündür.

Funksional tənlik
Funksional tənlik — məchulu funksiya olan tənlik.
Axtarılan funksiya müəyyən əməliyyatlarla (mürəkkəb funksiyanın əmələ gəlməsi əməliyyatları ilə) verilən məlum funksiyalarla bağlı olur. Adətən, axtarılan funksiyanın aid olduğu funksiyalar sinfi göstərilir.
Məsələn,
f
(
x
+
y
)
=
f
(
x
)
+
f
(
y
)
{\displaystyle f(x+y)=f(x)+f(y)}
. Burada
f
{\displaystyle f}
axtarılan funksiyadır. Bu funksional tənliyin həlli
f
(
x
)
=
α
x
{\displaystyle f(x)=\alpha x}
funksiyasıdır(əgər tənliyin həlli kəsilməz funksiyalar sinfinə aiddirsə).
f
(
x
y
)
=
f
(
x
)
+
f
(
y
)
{\displaystyle f(xy)=f(x)+f(y)}
və
f
(
x
+
y
)
=
f
(
x
)
⋅
f
(
y
)
{\displaystyle f(x+y)=f(x)\centerdot f(y)}
tənliklərinin kəsilməz həlləri, uyğun olaraq,
y
=
l
n
x
{\displaystyle y=lnx}
və
y
=
e
x
{\displaystyle y=e^{x}}
funksiyalarıdır.
Tək və cüt funksiyaların, dövri funksiyaların tərifləri funksional tənliklər vasitəsilə verilir.
Funksional əlaqələr
Hidrometeoroloji hadisə və proseslər çoxsaylı amillərin təsiri altında formalaşır. Bu hadisə və prosesləri öyrəndikdə, onlarla müxtəlif amillər arasındakı əlaqələr təhlil olunur. Ararılan tədqiqatlar iki tip məsləni həll etməyi imkan verir:
Funksional əlaqələr
Staxastik əlaqələr
Birinci tip məsələ, hidrometeoroloji hadisə və ona təsir edən amillərin ərazi üzrə və zamana görə dəyişmə səbəblərinin müəyyən edilməsi ilə əlaqədardır
İkinci tip məsələ isə, baxılan və ya prosesin inkişaf tendensiyası və ya onların konkret kəmiyyət göstəricisinin təyini ilə bağlıdır.
Y və X təsadüfi kəmiyyətlər arasındakı əlaqələr və onların sıxlığından asılı olaraq iki qrupa bölünür: funksional və Staxastik əlaqələr. Funksional asılıqlarda perdiktorun, x, hər bir qiymətinə, predikdiktantın, y, yalnız bir qiyməti uyğun olur, yəni bütün müşahidə nöqtələri əlaqə xətti üzərində yerləşir.
Funksionalizm (etnologiya)
Funksionalizm — etnologiya sahəsində XX əsrin əvvəllərində meydana gəlmiş sosioloji məktəb.
Etnologiyada funksionalizm sosioloji məktəbin prinsiplərinin sonrakı inkişafının məntiqi nəticəsi idi. Əgər diffuzionizmin vətəni Almaniya, sosiologiyanın vətəni Fransa idisə, funksionalizm istiqaməti İngiltərədə yaranmışdı və nə qədər geniş yayılsa da, ingilis nəzəriyyəsi olaraq qalırdı.
Funksionalizm məktəbin tədqiqat obyektinə istənilən ictimai institutun malik olduğu və birbaşa onun saxlanılmasına xidmət edən funksiyaların öyrənilməsi daxildir. Bu məktəb XX əsrin 20-ci illərində İngiltərədə etnologiyada əsas yer tuturdu.
İlk funksionalizm nəzəriyyəsini alman etnoloqu R. Turnvald 1911-ci ildə irəli sürmüşdür. Lakin funksionalizmin mövqeyi Böyük Britaniyada daha güclü oldu. Burada Malinovskinin rəhbərliyi altında XX əsrin 20-ci illərindən etibarən tezislər irəli sürülməyə başlandı. Malinovskinin ilk tezisi belə idi: mədəniyyəti onun cizgilərinə görə deyil, institutlarına görə təhlil etmək lazımdır. O bildirirdi ki, parlament idarəçiliyi mədəniyyətin mühüm elementi hesab edilir və çinlilərdə istifadə edilən çubuqlar isə yalnız qida prosesində kiçik bir elementdir.

Funksionalizm (memarlıq)
Funksionalizm — XX əsr memarlıq cərəyanıdır. Almaniyada ("Bauhauz" məktəbi) və Niderlandda yaranmışdır. Funksionalizm 1910-1920-ci illərin konstruktivizmi və avanqard bədii hərəkatı əsasında formalaşdı və 1930-cu illərdə müstəqil bir memarlıq üslubu kimi formalaşdı. Məsələn, Rusiya inqilabının, utopik anlayışları və idealist fikirləri funksionalizmin hüdudlarında əks etdirən konstruktivizmdən fərqli olaraq, memarlar formulaya uyğun olaraq konkret utilitar-konstruktiv vəzifələri həll etdilər: funksiya - tikinti - forma - keyfiyyət.
Qərbi Avropa funksionallığı ideyaları yeni materialların və tikinti texnologiyalarının istehsalında elmi və texnoloji tərəqqinin ehtiyaclarından əmələ gəlmişdir. Funksionalizm prinsipləri bina və tikililərin sənaye və məişət proseslərinə və onlarda olan funksiyaların (utilitar, kommunikativ, sosial-mədəni) ciddi şəkildə uyğunlaşdırılmasını nəzərdə tutur. Funksionalizmin mənşəyi ənənəvi ingilis evinin "rasional memarlıq" ənənələrinə, V. Morrisin və "İncəsənət və sənətkarlıq" emalatxanalarına, J. Hoffman, L. Bauer və K. Moserin Vyana emalatxanalarına, G. Muteisusun nəzəri görüşlərinə və alman Verkbundun fəaliyyətinə əsaslanır. Funksionalizm prinsipləri ən çox Almaniyada bauhauz məktəblərində və Niderlandda de steil dərnəyində inkişaf etmişdir. Xüsusi əhəmiyyət daşıyan Gottfried Semper və onun "Praktik Estetika", P. Behrens və O. Vaqerin əsərləri olmuşdur.
Fəaliyyətlilik, məqsədləri, ərazi şəraiti və ətraf mühit tələblərindən asılı olaraq ev tikməyə imkan verdi.
Funksionalizm (sosiologiya)
Funksionalizm — sosioloji məktəb, cərəyan.
Etnologiyada funksionalizm sosioloji məktəbin prinsiplərinin sonrakı inkişafının məntiqi nəticəsi idi. Əgər diffuzionizmin vətəni Almaniya, sosiologiyanın vətəni Fransa idisə, funksionalizm istiqaməti İngiltərədə yaranmışdı və nə qədər geniş yayılsa da, ingilis nəzəriyyəsi olaraq qalırdı. Bunun da özünün siyasi səbəbləri vardı.
Funksionalizm məktəbin tədqiqat obyektinə istənilən ictimai institutun malik olduğu və birbaşa onun saxlanılmasına xidmət edən funksiyaların öyrənilməsi daxildir. Bu məktəb XX əsrin 20-ci illərində İngiltərədə etnologiyada əsas yer tuturdu.
İlk funksionalizm nəzəriyyəsini alman etnoloqu R. Turnvald 1911-ci ildə irəli sürmüşdür. Amma funksionalizmin mövqeyi Böyük Britaniyada daha güclü oldu.
Burada Malinovskinin rəhbərliyi altında XX əsrin 20-ci illərindən etibarən tezislər irəli sürülməyə başlandı. Malinovskinin ilk tezisi belə idi: mədəniyyəti onun cizgilərinə görə deyil, institutlarına görə təhlil etmək lazımdır.
Funksiya (riyaziyyat)
Funksiya —
X
{\displaystyle X}
çoxluğunun hər bir elementinə qarşı
Y
{\displaystyle Y}
çoxluğunun bir elementini uyğun qoyan
F
{\displaystyle F}
münasibəti. Bu zaman
X
{\displaystyle X}
çoxluğu
F
{\displaystyle F}
funksiyasının təyin oblastı,
Y
{\displaystyle Y}
çoxluğu isə qiymətlər oblastı adlanır.
F
{\displaystyle F}
funksiyasının
X
{\displaystyle X}
çoxluğunu
Y
{\displaystyle Y}
çoxluğuna qarşı qoyması aşağıdakılardan hər hansı biri ilə işarə olunur:
F
:
X
→
Y
{\displaystyle F\colon X\to Y}
;
X
⟶
F
Y
{\displaystyle X{\stackrel {F}{\longrightarrow }}Y}
;
y
=
F
(
x
)
{\displaystyle y=F(x)}
;
F
:
x
↦
y
{\displaystyle F\colon x\mapsto y}
;
x
⟼
F
y
{\displaystyle x{\stackrel {F}{\longmapsto }}y}
.
f(x)=Burada x dəyişəni asılı olmayandır, y isə asılı dəyişəndir.
Funksiya 3 üsulla verilir:analitik, cədvəl və qrafik.
Tək funksiya
Funksiya f(-x)=-f(x) şərtini ödəyərsə belə funksiyaya tək funksiya deyilir. Məsələn y=3x funksiyası tək funksiyadır.
Qeyd: Tək funksiyanın qrafiki koordinat başlanğıcına, yəni (0,0) nöqtəsinə nəzərən; cüt funksiyanın qrafiki ordinat oxuna, yeni Oy oxuna nəzərən simmetrik olur.
Qeyd: Triqonometrik funksiyaların təkliyi və ya cütlüyü:
sin(-x)=-sinx (tək)
cos(-x)=cosx (cüt)
tg(-x)=-tgx (tək)
ctg(-x)=-ctgx (tək)
3) Funksiyanın artması və azalması:
X çoxluğunda arqumentin böyük qiymətinə funksiyanın böyük qiyməti uyğun gələrsə, f funksiyasına bu çoxluqda artan, arqumentin böyük qiymətinə funksiyanın kiçik qiyməti uyğun gələrsə, f funksiyasına bu çoxluqda azalan funksiya deyilir.
Yeni, x1, x2€X şərtində x1<x2 , f(x1)<f(x2) isə, funksiya artan olur.

Funksiya strukturu
Funksiya strukturu — Ümumiləşdirilmiş fraza quruluşu qrammatikası, baş əsaslı fraza quruluşu qrammatikası və leksik funksional qrammatika kimi fraza quruluşu qrammatikalarında xüsusiyyət strukturu mahiyyətcə atribut-qiymət cütləri toplusudur. Məsələn, nömrə adlı atributun tək dəyəri ola bilər. Atribut dəyəri ya atom ola bilər, məs. tək və ya kompleksdəki bir xarakter (əksər hallarda bu xüsusiyyət strukturudur, həm də siyahı və ya dəstdir).
Xüsusiyyət strukturu, qovşaqları dəyişənlərin dəyərlərinə və dəyişən adlarına gedən yollara uyğun gələn yönəldilmiş asiklik qrafik (DAG) kimi təqdim edilə bilər. Obyekt strukturlarında müəyyən edilmiş əməliyyatlar, məs. birləşmələrdən fraza quruluşu qrammatikalarında geniş istifadə olunur. Əksər nəzəriyyələrdə (məsələn, HPSG), xüsusiyyət strukturları adətən qeyri-rəsmi istifadə olunsa da, əməliyyatlar xüsusiyyət strukturlarının özlərində deyil, ciddi şəkildə xüsusiyyət strukturlarını təsvir edən tənliklər üzərində müəyyən edilir.
Burada iki "kateqoriya" və "razılaşma" funksiyası var. "Kateqoriya" "nominal ifadə" dəyərinə malikdir, "razılaşma" dəyəri isə "rəqəm" və "şəxs" xüsusiyyətlərinin "tək" və "üçüncü" olduğu başqa xüsusiyyət strukturu ilə göstərilir.

Funksiyaların kompozisiyası və ya mürəkkəb funksiya
Fərz edək ki,
f
{\displaystyle f}
funksiyası
A
{\displaystyle A}
çoxluğunu
B
{\displaystyle B}
çoxluğuna çevirir.
g
{\displaystyle g}
funksiyası isə
B
{\displaystyle B}
çoxluğunu
C
{\displaystyle C}
çoxluğuna çevirir. Yəni
x
∈
A
{\displaystyle x\in A}
olduqda
f
(
x
)
∈
B
{\displaystyle f(x)\in B}
,
y
∈
B
{\displaystyle y\in B}
olduqda isə
g
(
y
)
∈
C
{\displaystyle g(y)\in C}
olur. Beləliklə bu iki funksiyanın ardıcıl tətbiqi ilə
A
{\displaystyle A}
çoxluğunu
C
{\displaystyle C}
çoxluğuna çevrilir. Bu iki funksiyanın ardıcıl tətbiqi nəticəsində
A
{\displaystyle A}
çoxluğunu
C
{\displaystyle C}
çoxluğuna çevirən funksiyaya
f
{\displaystyle f}
və
g
{\displaystyle g}
funksiyalarının kompozisiyası deyilir və
g
∘
f
=
g
(
f
(
x
)
)
{\displaystyle g\circ f=g(f(x))}
kimi işarə olunur.
h
=
g
∘
f
{\displaystyle h=g\circ f}
funksiyasına mürəkkəb funksiya deyilir. Eyni qayda ilə üç və daha artıq funksiyanın kompozisiyası təyin olunur.
Funksiyanın diferensialı
Diferensial funksiyanın xətti artımını təsvir edir. Bu anlayış istiqamətdən asılı olaraq törəmə ilə sıx bağlıdır.
Funksiyanın
f
{\displaystyle f}
diferensialı
d
f
{\displaystyle df}
, onun
x
{\displaystyle x}
nöqtəsindəki qiyməti
d
x
f
{\displaystyle d_{x}f}
ilə işarə olunur.
Diferensialın sadə şəkildə izahı belədir: Verilmiş
f
(
x
)
{\displaystyle f(x)}
funksiyasının dəyişmə tezliyi onun arqumentinin (
x
{\displaystyle x}
) dəyişmə tezliyindən asılıdır.
Diferensial anlayışı XVII-XVIII əsrlərdə diferensial hesablarının yaranması zamanı daxil edilmişdir. XIX əsrdən başlayaraq analiz A.L.Kauçi və Karl Vayerstrass tərəfindən sərhəd qiymətləri əsasında yenidən işlənərək riyazi cəhətdən daha düzgün qurulmuşdur. Bununla diferensial anlayışı öz ilkin əhəmiyyətini itirir. Hazırda diferensial
d
x
{\displaystyle dx}
yalnız məhdud halda tətbiq olunur.
y
=
f
(
x
)
{\displaystyle y=f(x)}
funksiyası
(
a
,
b
)
{\displaystyle (a,b)}
intervalında diferensiallanandır.
Δ
y
=
f
′
(
x
)
Δ
x
+
(
Δ
x
)
Δ
x
{\displaystyle \Delta y=f'(x)\Delta x+(\Delta x)\Delta x}
Diferensiallanan
y
=
f
(
x
)
{\displaystyle y=f(x)}
funksiyasının
x
{\displaystyle x}
nöqtəsindəki artımının baş hissəsinə, yəni
Δ
x
{\displaystyle \Delta x}
-dən xətti asılı olan
f
′
(
x
)
Δ
x
{\displaystyle f'(x)\Delta x}
ifadəsinə onun
x
{\displaystyle x}
nöqtəsində diferensialı deyilir.

Funksiyanın qrafiki
Riyaziyyatda bir f funksiyanın qrafiki, bütün ( x, f ( x)) sıralı cütlərinin meydana gətirdiyi bir qrafikdir.
Elm, mühəndislik, texnologiya, maliyyə və digər sahələrdə qrafiklər bir çox məqsəd üçün istifadə edilir.
Bir dəyişənli funksiyanın qrafiki belədir:
f
(
x
)
=
{
a
,
x
=
1
i
c
i
n
d
,
x
=
2
i
c
i
n
c
,
x
=
3
i
c
i
n
.
{\displaystyle f(x)=\left\{{\begin{matrix}a,&{\mbox{ }}x=1{\mbox{ }}icin\\d,&{\mbox{ }}x=2{\mbox{ }}icin\\c,&{\mbox{ }}x=3{\mbox{ }}icin.\end{matrix}}\right.}
Buradakı sıralı cütlər belə ifadə edilir:
{(1, a), (2, d), (3, c)}
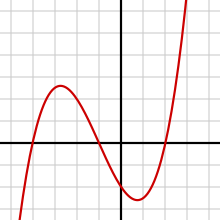
Həqiqi ədələr olan üçüncü dərəcədən bir çoxhədliin qrafiki belədir:
f
(
x
)
=
x
3
−
9
x
{\displaystyle f(x)={{x^{3}}-9x}\!\ }
Bunun sıralı cütləri belə ifadə edilir:
{( X, x 3 -9 x): x, bir həqiqi ədəddir}.
Bu çoxluq əgər karteziyan koordinant sistemində çəkilərsə, yandakı şəkildəki kimi bir əyri olar.
Bütün həqiqi ədədlər triqonometrik funksiyanın qrafiki belədir:
F ( x, y) = sin ( x 2 ) · cos ( y 2 )
Bunun verilənlər:
{( X, y, sin ( x 2 ) · cos (' 'y 2 )): x və y, həqiqi ədədlərdir.
Bu çoxluq əgər karteziyan koordinant sistemi ndə çəkilərsə, yandakı şəkildəki kimi bir səth olar.
İki ölçülü (X, Y) karteziyan koordinat sistemindəki bu çoxluqda, üçüncü koordinat (Z) ilə birlikdə görmək üçün rəng istifadə edilər.
x
=
x
1
,
…
,
x
n
{\displaystyle x=x_{1},\dotsc ,x_{n}}
formasında n dəyişənli bir f funksiyasının normalinin qrafiki belədir:
(
∇
f
,
−
1
)
{\displaystyle (\nabla f,-1)}
(Bir sabit ilə hasili). Bunu görmək üçün,
g
(
x
,
z
)
=
f
(
x
)
−
z
{\displaystyle g(x,z)=f(x)-z}
funksiyasının bir kümedeki qrafikini göz qarşısında saxlamaq və çoxluqda
∇
g
{\displaystyle \nabla g}
normalından istifadə etmək lazımdır.
Heş funksiya
Heş funksiya (Heşləşdirmə. ing. – hashing, rus - xеширование) – istənilən uzunluqlu giriş verilənlərin sabit uzunluqlu ikili sətirə elə çevrilməsidir ki, giriş verilənlərdə hər hansı dəyişiklik (hətta ən kiçik dəyişiklik də) çıxış sətirində ciddi dəyişiklik etsin. Bu çevrilmə adətən heş funksiya və ya bürünmə funksiyası , onun nəticəsi isə heş, heş- kod və ya məlumatın daycesti (ingiliscə message digest) və ya “məlumatın izi” (rus dilində “отпечаткa сообшения”) adlanır.
Əliquliyev R.M., Ağayev N.B., Alıquliyev R.M., Plagiatlıqla mübarizə texnologiyaları // Bakı. İnformasiya Texnologiyaları nəşriyyatı. 2015.

Hiks tələb funksiyası
Mikroiqtisadiyyatda istehlakçının Hiks tələbinə müvafiqliyi ona təyin edilmiş fayda gətirən və xərclərini minimallaşdıran məhsulların dəstəsinə tələbi bildirir. Əgər bu müvafiqlik müəyyən bir funksiyadır, onda ona Hiks tələb funksiyası, və ya əvəzini verən tələb funksiyası deyilir. Funksiya Con Hiks (John Hicks) şərəfinə adlandırılmışdır.
Riyazi şəkildə:
h
(
p
,
u
¯
)
=
arg
min
x
∑
i
p
i
x
i
{\displaystyle h(p,{\bar {u}})=\arg \min _{x}\sum _{i}p_{i}x_{i}}
s
u
c
h
t
h
a
t
u
(
x
)
≥
u
¯
{\displaystyle {\rm {such\ that}}\ \ u(x)\geq {\bar {u}}}
Harda ki h(p,u) Hiks tələb funksiyasıdır, və ya tələb olunan məhsul dəstəsidir, p qiymətləri səviyyəsidir, və
u
¯
{\displaystyle {\bar {u}}}
faydadır. Burda p qiymətlərin vektorudur, və X tələb olunan miqdarların vektorudur. Deməli bütün pixi cəmi X məhsullarına gedən ümumi xərcdir.
Hiks tələb funksiyaları riyazi hesablarda işlətmək asandır çünki onlar gəlirin olduğunu tələb etmirlər. Əlavə olaraq, minimallaşdırılmış olmalı funksiya
x
i
{\displaystyle x_{i}}
üzrə xəttidir, və bu optimizasiya problemini asanlaşdırır.
Amma verilmiş p qiymətləri və
w
{\displaystyle w}
gəliri ilə tələbi təsvir edən
x
(
p
,
w
)
{\displaystyle x(p,w)}
Marşal tələb funksiyasını birbaşa müşahidə etmək daha asandır. Hər ikisi bir biri ilə adi şəkildə əlaqədədir:
h
(
p
,
u
)
=
x
(
p
,
e
(
p
,
u
)
)
,
{\displaystyle h(p,u)=x(p,e(p,u)),\ }
Harda
e
(
p
,
u
)
{\displaystyle e(p,u)}
məxaric funksiyasıdır (verilmiş fayda əldə etmək üçün minimal gəliri göstərən funksiya)
h
(
p
,
v
(
p
,
w
)
)
=
x
(
p
,
w
)
,
{\displaystyle h(p,v(p,w))=x(p,w),\ }
Harda
v
(
p
,
w
)
{\displaystyle v(p,w)}
vasitəli fayda funksiyasıdır (verilmiş qiymətlər və müəyyən gəlir ilə əldə edilən faydanı göstərən funksiya).

Hiperbolik funksiyalar
Hiperbolik funksiyalar - elementar funksiyalar ailəsindəndir.Triqonometrik funksiyaların analoqu sayılır.Əsas Hiperbolik funksiyalar bunlardır:
Hiperbolik sinus
Hiperbolik kosinus
Hiperbolik tangens
Hiperbolik kotangens
Tərs Hiperbolik funksiyalar isə bunlardır:
Hiperbolik arksinus
Hiperbolik arkskosinus
Hiperbolik arkstangens
Hiperbolik arkskotangens
Hiperbolik funksiyalar aşağıdakı funksiyalardan ibarətdir:
Hiperbolik sinus:
sinh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
2
=
e
2
x
−
1
2
e
x
{\displaystyle \sinh x={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{2}}={\frac {e^{2x}-1}{2e^{x}}}}
Hiperbolik kosinus:
cosh
x
=
e
x
+
e
−
x
2
=
e
2
x
+
1
2
e
x
{\displaystyle \cosh x={\frac {e^{x}+e^{-x}}{2}}={\frac {e^{2x}+1}{2e^{x}}}}
Hiperbolik tangens:
tanh
x
=
sinh
x
cosh
x
=
e
x
−
e
−
x
e
x
+
e
−
x
=
e
2
x
−
1
e
2
x
+
1
{\displaystyle \tanh x={\frac {\sinh x}{\cosh x}}={\frac {e^{x}-e^{-x}}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{2x}-1}{e^{2x}+1}}}
Hiperbolik kotangens:
coth
x
=
cosh
x
sinh
x
=
e
x
+
e
−
x
e
x
−
e
−
x
=
e
2
x
+
1
e
2
x
−
1
{\displaystyle \coth x={\frac {\cosh x}{\sinh x}}={\frac {e^{x}+e^{-x}}{e^{x}-e^{-x}}}={\frac {e^{2x}+1}{e^{2x}-1}}}
Hiperbolik sekans:
sech
x
=
(
cosh
x
)
−
1
=
2
e
x
+
e
−
x
=
2
e
x
e
2
x
+
1
{\displaystyle \operatorname {sech} \,x=\left(\cosh x\right)^{-1}={\frac {2}{e^{x}+e^{-x}}}={\frac {2e^{x}}{e^{2x}+1}}}
Hiperbolik kosekans:
csch
x
=
(
sinh
x
)
−
1
=
2
e
x
−
e
−
x
=
2
e
x
e
2
x
−
1
{\displaystyle \operatorname {csch} \,x=\left(\sinh x\right)^{-1}={\frac {2}{e^{x}-e^{-x}}}={\frac {2e^{x}}{e^{2x}-1}}}
Hiperbolik funksiyalar xəyali vahid (i) dairəsi ilə aşağıdakı kimi də ifade edilir:
Hiperbolik sinus:
sinh
x
=
−
i
sin
i
x
{\displaystyle \sinh x=-{\rm {i}}\sin {\rm {i}}x\!}
Hiperbolik kosinus:
cosh
x
=
cos
i
x
{\displaystyle \cosh x=\cos {\rm {i}}x\!}
Hiperbolik tangens:
tanh
x
=
−
i
tan
i
x
{\displaystyle \tanh x=-{\rm {i}}\tan {\rm {i}}x\!}
Hiperbolik kotangens:
coth
x
=
i
cot
i
x
{\displaystyle \coth x={\rm {i}}\cot {\rm {i}}x\!}
Hiperbolik sekans:
sech
x
=
sec
i
x
{\displaystyle \operatorname {sech} \,x=\sec {{\rm {i}}x}\!}
Hiperbolik kosekans:
csch
x
=
i
csc
i
x
{\displaystyle \operatorname {csch} \,x={\rm {i}}\,\csc \,{\rm {i}}x\!}
i, i2 = −1 - xəyali vahiddir.
d
d
x
sinh
x
=
cosh
x
{\displaystyle {\frac {d}{dx}}\sinh x=\cosh x\,}
d
d
x
cosh
x
=
sinh
x
{\displaystyle {\frac {d}{dx}}\cosh x=\sinh x\,}
d
d
x
tanh
x
=
1
−
tanh
2
x
=
sech
2
x
=
1
/
cosh
2
x
{\displaystyle {\frac {d}{dx}}\tanh x=1-\tanh ^{2}x={\hbox{sech}}^{2}x=1/\cosh ^{2}x\,}
d
d
x
coth
x
=
1
−
coth
2
x
=
−
csch
2
x
=
−
1
/
sinh
2
x
{\displaystyle {\frac {d}{dx}}\coth x=1-\coth ^{2}x=-{\hbox{csch}}^{2}x=-1/\sinh ^{2}x\,}
d
d
x
csch
x
=
−
coth
x
csch
x
{\displaystyle {\frac {d}{dx}}\ {\hbox{csch}}\,x=-\coth x\ {\hbox{csch}}\,x\,}
d
d
x
sech
x
=
−
tanh
x
sech
x
{\displaystyle {\frac {d}{dx}}\ {\hbox{sech}}\,x=-\tanh x\ {\hbox{sech}}\,x\,}
d
d
x
arsinh
x
=
1
x
2
+
1
{\displaystyle {\frac {d}{dx}}\,\operatorname {arsinh} \,x={\frac {1}{\sqrt {x^{2}+1}}}}
d
d
x
arcosh
x
=
1
x
2
−
1
{\displaystyle {\frac {d}{dx}}\,\operatorname {arcosh} \,x={\frac {1}{\sqrt {x^{2}-1}}}}
d
d
x
artanh
x
=
1
1
−
x
2
{\displaystyle {\frac {d}{dx}}\,\operatorname {artanh} \,x={\frac {1}{1-x^{2}}}}
d
d
x
arcsch
x
=
−
1
|
x
|
1
+
x
2
{\displaystyle {\frac {d}{dx}}\,\operatorname {arcsch} \,x=-{\frac {1}{\left|x\right|{\sqrt {1+x^{2}}}}}}
d
d
x
arsech
x
=
−
1
x
1
−
x
2
{\displaystyle {\frac {d}{dx}}\,\operatorname {arsech} \,x=-{\frac {1}{x{\sqrt {1-x^{2}}}}}}
d
d
x
arcoth
x
=
1
1
−
x
2
{\displaystyle {\frac {d}{dx}}\,\operatorname {arcoth} \,x={\frac {1}{1-x^{2}}}}
∫
sinh
a
x
d
x
=
a
−
1
cosh
a
x
+
C
{\displaystyle \int \sinh ax\,dx=a^{-1}\cosh ax+C}
∫
cosh
a
x
d
x
=
a
−
1
sinh
a
x
+
C
{\displaystyle \int \cosh ax\,dx=a^{-1}\sinh ax+C}
∫
tanh
a
x
d
x
=
a
−
1
ln
(
cosh
a
x
)
+
C
{\displaystyle \int \tanh ax\,dx=a^{-1}\ln(\cosh ax)+C}
∫
coth
a
x
d
x
=
a
−
1
ln
(
sinh
a
x
)
+
C
{\displaystyle \int \coth ax\,dx=a^{-1}\ln(\sinh ax)+C}
∫
d
u
a
2
+
u
2
=
sinh
−
1
(
u
a
)
+
C
{\displaystyle \int {\frac {du}{\sqrt {a^{2}+u^{2}}}}=\sinh ^{-1}\left({\frac {u}{a}}\right)+C}
∫
d
u
u
2
−
a
2
=
cosh
−
1
(
u
a
)
+
C
{\displaystyle \int {\frac {du}{\sqrt {u^{2}-a^{2}}}}=\cosh ^{-1}\left({\frac {u}{a}}\right)+C}
∫
d
u
a
2
−
u
2
=
a
−
1
tanh
−
1
(
u
a
)
+
C
;
u
2
<
a
2
{\displaystyle \int {\frac {du}{a^{2}-u^{2}}}=a^{-1}\tanh ^{-1}\left({\frac {u}{a}}\right)+C;u^{2}<a^{2}}
∫
d
u
a
2
−
u
2
=
a
−
1
coth
−
1
(
u
a
)
+
C
;
u
2
>
a
2
{\displaystyle \int {\frac {du}{a^{2}-u^{2}}}=a^{-1}\coth ^{-1}\left({\frac {u}{a}}\right)+C;u^{2}>a^{2}}
∫
d
u
u
a
2
−
u
2
=
−
a
−
1
sech
−
1
(
u
a
)
+
C
{\displaystyle \int {\frac {du}{u{\sqrt {a^{2}-u^{2}}}}}=-a^{-1}\operatorname {sech} ^{-1}\left({\frac {u}{a}}\right)+C}
∫
d
u
u
a
2
+
u
2
=
−
a
−
1
csch
−
1
|
u
a
|
+
C
{\displaystyle \int {\frac {du}{u{\sqrt {a^{2}+u^{2}}}}}=-a^{-1}\operatorname {csch} ^{-1}\left|{\frac {u}{a}}\right|+C}
C sabit ədəddir.
arsinh
x
=
ln
(
x
+
x
2
+
1
)
{\displaystyle \operatorname {arsinh} \,x=\ln \left(x+{\sqrt {x^{2}+1}}\right)}
arcosh
x
=
ln
(
x
+
x
2
−
1
)
;
x
≥
1
{\displaystyle \operatorname {arcosh} \,x=\ln \left(x+{\sqrt {x^{2}-1}}\right);x\geq 1}
artanh
x
=
1
2
ln
1
+
x
1
−
x
;
|
x
|
<
1
{\displaystyle \operatorname {artanh} \,x={\tfrac {1}{2}}\ln {\frac {1+x}{1-x}};\left|x\right|<1}
arcoth
x
=
1
2
ln
x
+
1
x
−
1
;
|
x
|
>
1
{\displaystyle \operatorname {arcoth} \,x={\tfrac {1}{2}}\ln {\frac {x+1}{x-1}};\left|x\right|>1}
arsech
x
=
ln
1
+
1
−
x
2
x
;
0
<
x
≤
1
{\displaystyle \operatorname {arsech} \,x=\ln {\frac {1+{\sqrt {1-x^{2}}}}{x}};0<x\leq 1}
arcsch
x
=
ln
(
1
x
+
1
+
x
2
|
x
|
)
{\displaystyle \operatorname {arcsch} \,x=\ln \left({\frac {1}{x}}+{\frac {\sqrt {1+x^{2}}}{\left|x\right|}}\right)}
sinh
x
=
x
+
x
3
3
!
+
x
5
5
!
+
x
7
7
!
+
⋯
=
∑
n
=
0
∞
x
2
n
+
1
(
2
n
+
1
)
!
{\displaystyle \sinh x=x+{\frac {x^{3}}{3!}}+{\frac {x^{5}}{5!}}+{\frac {x^{7}}{7!}}+\cdots =\sum _{n=0}^{\infty }{\frac {x^{2n+1}}{(2n+1)!}}}
cosh
x
=
1
+
x
2
2
!
+
x
4
4
!
+
x
6
6
!
+
⋯
=
∑
n
=
0
∞
x
2
n
(
2
n
)
!

Kobb-Duqlas istehsal funksiyası
Amerikan alimləri Ç.Kobb və P.Duqlasın adları ilə bağlı yaratdıqları «Kobb-Duqlas funksiyası» ekonometrik nailiyyətlərin ən geniş tətbiq məhsullarındandır. ABŞ-nin XX əsrin 20-ci illərində emal sənayesinə hesablanan «Kobb-Duqlas funksiyası» istehsal həcminin istehsalın əsas faktorları əmək və kapitaldan asılılığını ifadə edir. Bu funksiyaya görə istehsal həcmi iki faktorla istifadə edilən istehsal vasitələri kapital və əməyin miqdarı ilə təyin olunur.
İstehsal funksiyasının ümumi düsturu Y = AF(K,N) şəklindədir. Bununla belə, Kobb-Duqlas kimi spesifik düsturlar da mövcuddur: Y = AKθ N1-θ.
Burada (1-θ) və θ uyğun olaraq əmək və kapitalın gəlirdəki xüsusi çəkilərini göstərir. Kobb-Duqlas funksiyası iqtisadiyyatı dəqiq təsvir etdiyinə və riyazi cəhətdən asan təfsir olunduğuna görə iqtisadçılar tərəfindən geniş istifadə edilir. Məsələn, Kobb-Duqlas funksiyasından istifadə etməklə kapitalın marjinal məhsuldarlığını (KMM) aşağıdakı şəkildə ifadə edə bilərik: KMM = θAKθ-1 N1-θ = θA(K/N)-(1-θ) = θY/K
Kobb–Duqlas istehsal funksiyası qeyri xəttidir: Y = ALαKβε
Ancaq funksiyanın hər iki tərəfini təbii loqarifm götürməklə xətti hala transformasiya etmək mümkündür: lnY = lnA + αlnL + βlnK + lnε
Kobb-Duqlas funksiyasının başlıca cəhətləri aşağıdakılardır:
Mənfəətin və xərclərin xüsusi çəkisinin dəyişmədiyi, yığımın olmadığı və istehsalın (əmək və kapital) elastikliyinin vahidə bərabər olduğu fərz edilir;
İstehsal amillərinin bir-birini əvəz etmələri sıfırla vahid arasında tərəddüd edir və adətən vahiddən kiçikdir; Qarşılıqlı əvəzetmələrin hüdudu texniki inkişaf səviyyəsi ilə müəyyən edilir;
Əməyin kapital ilə əvəz olunması imkanları nəzəri cəhət-dən sonsuzdur;
İstehsal amilləri keyfiyyətinin dəyişməsi nəzərə alınmır, yəni, texniki tərəqqidən sərfnəzər edilir. Buradan da belə bir nəticə çıxarmaq olar ki, funksiya yalnız ekstensiv iqtisadi artım üçün münasibdir.
İstehsal funksiyalarının irəli sürülməsi tarixi sənayeləşmə dövrünə təsadüf edir.

